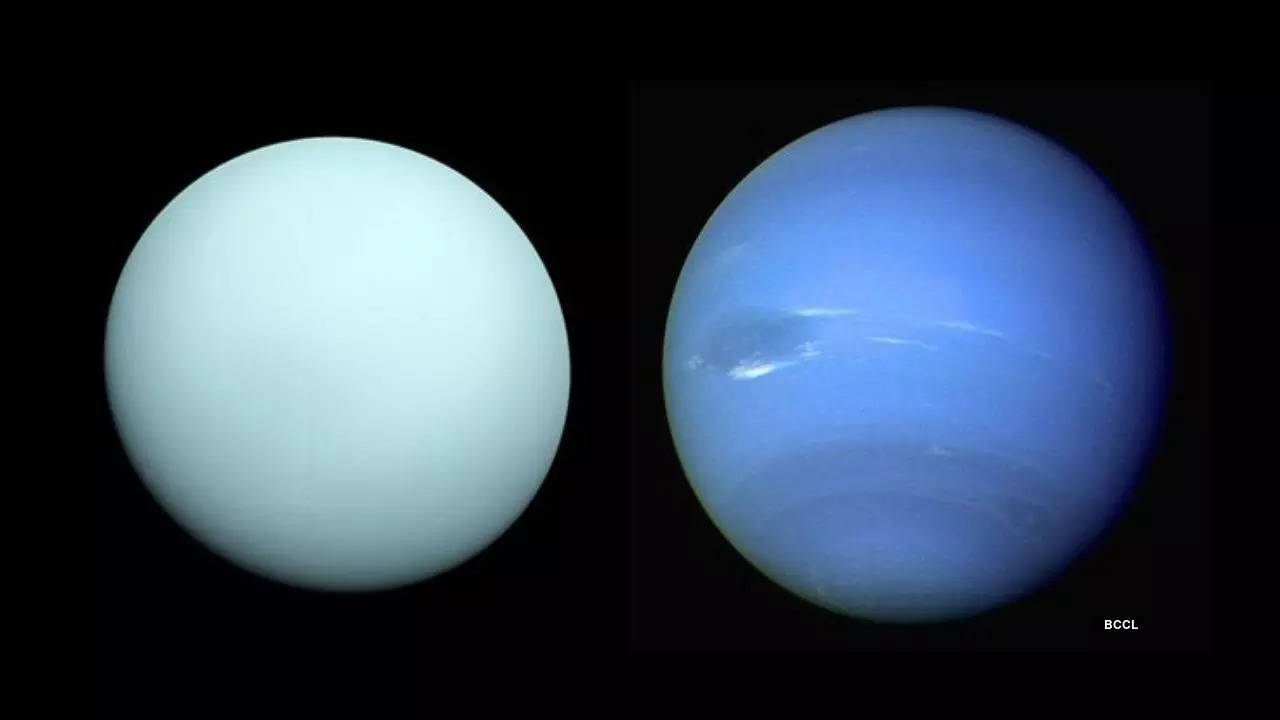
NEW DELHI: A latest analysis hinted at important presence of methane ice inside Uranus and Neptune which have lengthy been thought to be icy giants, presumed to be predominantly composed of frozen water.
In keeping with Area.com, the implications of this discovery lengthen past mere composition, doubtlessly unlocking the mysteries surrounding the formation of Uranus and Neptune.
Voyager 2’s solitary flyby within the Nineteen Eighties supplied a glimpse into Uranus and Neptune, leaving scientists with solely speculative notions of their make-up, together with substantial quantities of oxygen, carbon, and hydrogen.
Astronomers have constructed fashions primarily based on knowledge from Voyager 2 and terrestrial telescopes to delve deeper into the composition of those distant giants. These fashions sometimes posit a skinny envelope of hydrogen and helium, a dense layer of superionic water and ammonia, and a rocky core, incomes the planets their “ice large” designation. Nevertheless, additionally they counsel the potential for huge reservoirs of water, doubtlessly exceeding Earth’s oceans by tens of hundreds of occasions.
The most recent research challenges these typical fashions by contemplating the formation strategy of Uranus and Neptune. As these planets coalesced from the primordial photo voltaic nebula, they amassed planetesimals, paying homage to modern comets from the Kuiper Belt. In contrast to the presumed water-rich composition of the ice giants, these planetesimals are carbon-rich.
Addressing this puzzle, Uri Malamud, lead writer of the research and a planetary scientist at Technion – Israel Institute of Know-how, and his collaborators generated a whole lot of hundreds of inside fashions for Uranus and Neptune. Their algorithm sought to match noticed traits like radius and mass, incorporating numerous substances together with iron, water, and methane, the first part of pure gasoline.
Amongst these fashions, these that includes methane emerged as viable candidates, with the methane layer doubtlessly accounting for as much as 10% of the planet’s mass. This methane layer, located between the hydrogen-helium envelope and the water layer, might present a decision to the enigmatic origins of those distant giants.
The analysis, printed on the preprint server arXiv, means that methane ice could have shaped throughout the planets’ tumultuous formation, as hydrogen reacted with carbon within the accreted planetesimals. These reactions occurred underneath excessive situations of temperature and strain, mirroring the situations believed to prevail throughout the planets’ early improvement.
Whereas confirming the presence of methane is difficult, future missions proposed by Nasa and different area businesses could present the means to confirm these discoveries.
In keeping with Area.com, the implications of this discovery lengthen past mere composition, doubtlessly unlocking the mysteries surrounding the formation of Uranus and Neptune.
Voyager 2’s solitary flyby within the Nineteen Eighties supplied a glimpse into Uranus and Neptune, leaving scientists with solely speculative notions of their make-up, together with substantial quantities of oxygen, carbon, and hydrogen.
Astronomers have constructed fashions primarily based on knowledge from Voyager 2 and terrestrial telescopes to delve deeper into the composition of those distant giants. These fashions sometimes posit a skinny envelope of hydrogen and helium, a dense layer of superionic water and ammonia, and a rocky core, incomes the planets their “ice large” designation. Nevertheless, additionally they counsel the potential for huge reservoirs of water, doubtlessly exceeding Earth’s oceans by tens of hundreds of occasions.
The most recent research challenges these typical fashions by contemplating the formation strategy of Uranus and Neptune. As these planets coalesced from the primordial photo voltaic nebula, they amassed planetesimals, paying homage to modern comets from the Kuiper Belt. In contrast to the presumed water-rich composition of the ice giants, these planetesimals are carbon-rich.
Addressing this puzzle, Uri Malamud, lead writer of the research and a planetary scientist at Technion – Israel Institute of Know-how, and his collaborators generated a whole lot of hundreds of inside fashions for Uranus and Neptune. Their algorithm sought to match noticed traits like radius and mass, incorporating numerous substances together with iron, water, and methane, the first part of pure gasoline.
Amongst these fashions, these that includes methane emerged as viable candidates, with the methane layer doubtlessly accounting for as much as 10% of the planet’s mass. This methane layer, located between the hydrogen-helium envelope and the water layer, might present a decision to the enigmatic origins of those distant giants.
The analysis, printed on the preprint server arXiv, means that methane ice could have shaped throughout the planets’ tumultuous formation, as hydrogen reacted with carbon within the accreted planetesimals. These reactions occurred underneath excessive situations of temperature and strain, mirroring the situations believed to prevail throughout the planets’ early improvement.
Whereas confirming the presence of methane is difficult, future missions proposed by Nasa and different area businesses could present the means to confirm these discoveries.